Have you ever asked why the oversimplification of digital cameras? Could it be a case of Corporate Marketers selling the idea that it's the best way to present complex talking points like image quality, noise, dynamic range, and the different kinds of image sensors? Do you support this notion?
Why would one review this? Many photographers prefer to avoid technical discussions about digital cameras. They will follow social media advice or their experience to find the best settings for "ISO sensitivity," exposure, and exposure compensation. Corporate marketers prefer this state of mind when they design and manage commercial programs like the "size and capture" theory.
We are reviewing the benefits of having technical conversations versus focusing on specifications. My goal is not to critique but to review the benefits technical information adds to our "digital" journey. The images in this article were taken with different cameras, like E-Series and M43 Olympus cameras. The Enhanced Raw Files from Olympus were converted in Workspace and are best viewed on a large display. The converted raw files were exported as 16-bit Tiff files and prepped in PS...
This is one of the most exciting "minimalist" digital cameras, with fantastic Image Quality and more creative potential than the Fuji X100V.
The fast pace at which sensors and image processors evolved in the late 90s changed to more specific improvements from 2012 onwards. Interestingly, one of the exciting consumer trends in 2023 is the rediscovery of older cameras like the Olympus EM5 MKI and various other brands. It's also fascinating to see how reviewers and forum experts forget how they raved about older cameras like the Canon 5D III, the Nikon D800, and the Olympus EM5 MKI. Another example of this trend is the Canon 5D IV versus R6 "Color Science" conversation. See this
video on GAS and the 5D III in 2023...
When last did you see a Photographer taking +2 Million photos? See this fascinating
video.
From 2012, manufacturers focused more on sensor sensitivity, global shutter, rolling shutter (sensor readout speeds), auto-focussing, image processors, computational photography, and high-quality JPEG files. Another exciting trend is RAW files like the Enhanced Raw Format, Fuji's X Raw Studio, and the raw converter/editor combos from Luminar, PhotoLab, ION, and Photoshop.
Did you know Workspace and X Raw Studio let us review/edit our camera's "Raw" settings?
The Konica Minolta A2 (8MP CCD) from 2004 - ISO100, f3.5, 1/80 - taken 26th October and OOC Tiff file edited in Photoshop.
I've been photographing with the Konica Minolta A2 (2004) and the Canon PowerShot A720IS (2007) over the past 2 weeks. The A2 was my first "serious" digital camera, and both my son and I captured great memories and short videos with the Konica Minolta A2. I replaced the A2 with a Canon 350D and later added the Canon PowerShot G7 to my camera bag. The Canon A720IS reminds me of my trusty Canon G7. My journey with Olympus started with the Olympus E-410 (DSLR).
Image taken with the EM1 III, the 45mm f1.8 lens, a small product studio, and two Olympus FL600 flashlights in RC Mode.
Should the camera do everything, or is the photographer part of the image creation process? This is an important question for many readers. For example, some photographers get excellent results with older cameras like the Olympus EM5 MKI (16MP sensor). It's also no surprise to see great photos from even older cameras. Others rely on modern cameras with larger sensors. Why is the contrast between those relying on new technologies and those using older cameras so significant?
See this
example of an enthusiast's filming with a 2008 compact camera.
Another
example of a photographer enjoying older cameras...
Olympus Pen EM5 with 75 - 300mm 43.8-6.7 lens - ISO200, f4.8, 1/2000 - Enhanced Raw File converted in Workspace.
Why is oversimplification problematic? Does the OM-1 have a better IQ than the EM1 III, or does the OM-1 simply have different strengths and weaknesses? Many E-series Olympus cameras had an analog image look with so-called "Olympus Colors," while the E1, E3, and E5 were Pro Cameras. What's the difference? Image sensors and processors continued to improve, and so did Image Quality. Olympus shifted its focus to advanced features like computational photography as digital cameras matured from 2012 onwards. They were the first to introduce Live Time and Live Composite to the Olympus EM1 MKI. The Olympus EM1X & EM1 III introduced more advanced features and became two of the most capable computational digital cameras in 2019/20.
Source: Photography Blog - link. Also, see my comments on Rob Trek's forum.
Oversimplification is problematic when social media experts selectively discuss camera information. For example, most camera experts focus on marketing theories, specifications, and unscientific tests like comparing Live MOS with "inequivalent" Standard and BSI CMOS sensors. Some claim it's all part of dumbing down and prepping photographers for AI. It could also be a case of reviewers and forum moderators throttling the technical conversation for more advertising space. Whatever the reasons, most photographers see little value in technical information or the history of cameras.
See this article with my analysis of a recent Fuji X-H2 review -
link.
Olympus E-410 with 14 - 42mm Kit lens - ISO100, F9.0, 1/250 - Enhanced Raw converted with its analog feel in Workspace.
What is the difference between my information and the "size and capture" theory? Folks, I also use a simplified version of the camera's technical complexities. Why is my information different from the "size and capture" theory? My information was designed and developed over a 2 year period, while the theoretical fundamentals stayed consistent. This makes it possible to objectively explain digital cameras or any new developments. For example, the Panasonic S5 and Sony A7 III are both 24MP cameras with similar optical characteristics like Field of View and Bokeh.
The technical characteristics, however, are unique for each of these 2 cameras. This explains the differences between the sensor's saturation, dynamic range, and noise of the S5 and the A7 III. The "size and capture" theory claims that the Optical and Technical characteristics are the same for identical sensor sizes. For example, social media experts claim crop sensors have more noise or less dynamic range than full-frame sensors because crop sensors capture less light (size and capture theory). What they won't say is the sensor's image circle determines how much "light" the sensor receives. (optical differences) Both crop and full-frame sensors have a full view of the scene.
Why is the statement "one sensor captures more light" misleading? Manufacturers design sensors to saturate when they receive enough light. Full-frame and crop sensor lenses are designed to accurately project the reflected light from the subject to an invisible Image Circle covering the sensor. The sensor receives a focussed bundle of information that fills (exposes) the camera's sensor.
The camera's ability to capture a scene is a function of design and NOT size...
The fascinating Powershot A720 IS w 8MP CCD from 2007 - ISO80, f4.0, 1/250 - OOC jpeg was slightly edited and prepped in Photoshop.
Why is this important? Because it changes how we apply digital photography, prepare our cameras, and convert our Raw Files. For example, most photographers continue to use the Exposure Triangle to explain digital cameras. The exposure triangle's main weakness is its inability to communicate the significance of saturating the sensor. You would literally find no videos explaining this...
How many Olympus photographers know they can export their Olympus Colors to editors like PS with the Olympus Image Processor embedded in WS? These benefits of prepping our Enhanced Raw Files in an Olympus "ecosystem" are something all M43 photographers should know. In short, know-how lets us enjoy an elevated level of Olympus Image Quality, Color "Science," and Tonal Data.
Olympus EM1 III with 12 - 200mm f3.5 - 6.3 lens - ISO400, f7.1, 1/250 -
Pro Capture and the Enhanced Raw File converted in Workspace.
Quick test. Why don't more M43 photographers have conversations about the Pen F and EP-7's color and monochrome filters or the additional color tools of Workspace? The same applies to the Enhanced Raw Format and our ability to tweak our camera settings in Workspace. This also applies to Fuji's X Raw Studio. Why the silence about these raw converters and challenges with the "analog" exposure triangle? Everyone can do this basic test with Photoshop and Workspace. Open the same raw files with Photoshop and Workspace and calculate the number of times Photoshop or Lightroom shows clipped highlights and Workspace not. Would you find the same discrepancies with noise?
Olympus EM5 with the Lumix 14-45mm lens, ISO200, f6.3, 1/400 - Enhanced Raw File converted in Workspace.
Technical information reveals why Image Quality is NOT a function of sensor size. It also explains why we don't benefit from arguing which sensor has less noise or more DR. All digital cameras have noise and too little dynamic range. After all, they all have the same technical limitations.
Oversimplification is the norm when discussing cameras today. Phrases like "the larger one captures more light" are treated as "factually accurate." Nobody questions the technical validity of these oversimplified claims. It's like saying my motorcar is faster because it has bigger tires...
Even worse, marketers persuaded photographers to collectively "police" and prevent conversations about sensor size. Why do intelligent people allow this kind of behavior? How many critical and everyday topics are labeled "not open for public discussion" and policed by those affected most..?
Figure 2
1. Learning through reading and technical conversations..?
This section focuses on the technical conversation that could improve your image quality. Knowledge empowers people and is the difference between successful and average photography...
The lack of technical know-how became a big handicap for most digital photographers. For example, only some know that the sensor's saturation and SNR are critical, or that Standard CMOS, Live MOS, and BSI sensors are based on a CMOS architecture. Why should one discuss these sensor types, and why would one prefer a specific one? Because each one has unique advantages and disadvantages.
Olympus EP-2 with Kit lens - ISO200, f6.3, 1/125 - Raw converted in WS and 16-bit Tiff edited in PS.
Doesn't high ISO values imply we are under-exposing the sensor? An underexposed sensor tells us the sensor is less saturated with a lower SNR and more visible noise. The solution is not bigger sensors because they ALL have similar technical limitations. The main differences between image sensors are Quantum and Optical efficiencies, pixel area, and the sensor's noise floor. An informed reaction is to add more reflected light onto the sensor. How do we add more light to the sensor?
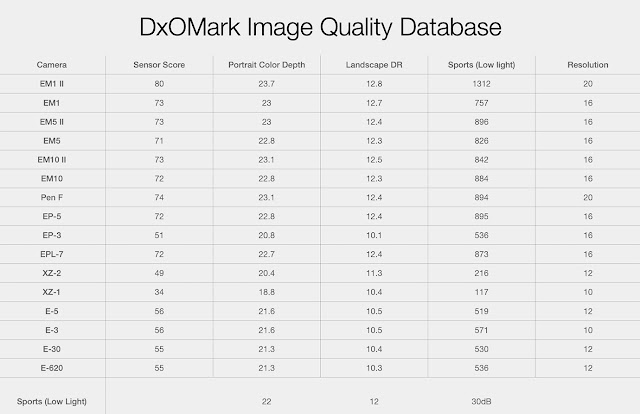
Study this
article on "How to read the DxOMark" test data...
How do we monitor the sensor's exposure level? The histogram was designed to display the sum of the sensor's exposure (shutter speed and aperture) and ISO amplification. Any fixed variables of the exposure formula are also displayed. How do we isolate the image sensor's "exposure" data? Change to "manual" ISO by selecting a fixed ISO. That means the aperture and shutter speed are the only remaining variables. I typically start my exposure process with an auto-exposure reading. I use that information to "optimize" my exposure settings, optical effects, and the image sensor...
See this article explaining the shutter and aperture functions and passing light onto the sensor...
Olympus EM5 and Lumix 14mm f2.5 lens, ISO200, f3.2, 1/320 - Enhanced Raw File converted and the Gamma curve adjusted in Workspace.
Stacked BSI sensors are Optically more Efficient and have higher readout speeds. They are perfect for bird-in-flight photography. It's one of the reasons the OM-1 and the Sony A1 are great BIF cameras. What do we learn from this? The real difference is functionality because image quality has long been excellent. Why do M43 cameras have a Live MOS sensor? The Pixel's Recording Area of Live MOS sensors is larger than the Standard CMOS equivalent because every 4 pixels have the same control wiring. This reduces the noise floor and increases the Sensitivity of Live MOS sensors.
Optical and Quantum Efficiency equals Sensor Sensitivity.
Only some M43 photographers learned that the sensor has an active noise floor when we turn the camera on. See the AST point in the graph (Fig. 1 below). We want to hide this noise floor by upping the sensor's saturation and SNR levels. For instance, the sensor receives less reflected light from shadow areas. This means a smaller image signal with a less saturated sensor, fewer tonal data, and a lower Signal to Noise ratio (SNR). This is why we see more noise in shadow areas...
Fewer tonal data, a lower SNR, and more visible noise...
The camera's exposure level (Aperture and Shutter Speed) determines the sensor's Saturation Level and Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) or the visibility of the Noise Floor. The final image will have less noise with more Reflected Light and more noise with less Reflected Light reaching the sensor. Your ISO does not adjust the sensor's sensitivity. It only amplifies the image signal and the SNR...
These unique technical characteristics apply to all sensor sizes.
See this video for excellent tips on various types of scenes.
An excellent video explaining how to set exposure.
Study this article for more information.
Figure 1. This is one of the best illustrations explaining and showing photographers how to control the image sensor.
Workspace illustrates the negative effect of a lack of knowledge. Only some M43 photographers mastered the unique benefits of working with Workspace. For example, the Standard Noise Filter in Workspace is the best option for Olympus RAW files. Workspace also lets us share editing and color profiles with fellow photographers. We also get access to the camera's image settings, the Olympus Image Processor, and the ability to tweak the camera's gamma curve in Workspace. For example, it lets us replicate and edit the camera's JPEG look with our PCs. Workspace is also the more user-friendly Raw converter for those interested in learning to work with raw files.
While the standard noise filter in Workspace is excellent, the new AI noise filter is a game changer. No other raw converter is more effective in processing Enhanced Raw Files than Workspace. With Workspace we can see the camera's final Live View image while testing the AI noise filter settings. For example, I was blown away from the results I get with my EM1 III when comparing my Canon 6D II to the EM1 III in similar lighting conditions at ISO6400 or ISO12800.
What is the Gamma Curve? The photons to electrons graph (Fig. 1) shows the linear nature of image sensors. The Gamma function converts this "linear" image data to match it to the human eye. For example, Viewer 3 had a Gamma function. The weakness of this function was it had fixed settings. That gave us limited control over shadows & highlights. Olympus improved this with Workspace as well as more recent Olympus cameras. We can now tweak the final Gamma Curve with the Shadows, Highlights, Midtones, Tone Curves (Workspace), and various Gradation options.
Olympus cameras and Workspace form an integrated solution with many benefits. No other raw converter, except Fuji's, offers this synergy between the camera and Raw Converter. Knowing this, why would any "honest" forum expert give incomplete or false feedback about Workspace?
Study this article for more about the Gradation Function.
Olympus EM5 MKII with Lumic 45-175mm PZ Lens - ISO200, f5.6, 1/1000 - Enhanced Raw converted in Workspace.
Does the Gamma function improve the camera's Dynamic Range? The best way to treat questions like these is to study my articles and understand the image-taking process. The illustration below shows how the Image Taking Processor applies the Gamma Curve (Tonal Response Curve) in step 2. That means the image sensor already captured the image and Dynamic Range in Step 1.
Which of PDAF or Contrast Detection AF is more efficient? Is the camera's AF requirements the same for video and photography? The tested camera's autofocus is not like Canon's. This is one of the most repeated statements in reviews. Does this apply to photography or only video applications? Are test videos with people running to the camera or jumping in and out of the FOV applicable to video or photography? For example, I would rather see a list of photography applications and a summary of the camera's autofocus abilities and efficiencies for each type of application.
One rarely knows which of the different AF applications reviewers or promoters tested. We only see meaningless one-line statements like "Sony's or Canon's tracking capability is superior." Again, does this apply to video or photography? Marketers created the same confusion on autofocus as they did with sensor size. I am working on a new article to discuss autofocus applications.
Each photographer has specific AF needs like Birding (BIF), travel, family, portrait, or landscape photography. This is one of the reasons why the Panasonic G9 is popular amongst M43 photographers and unpopular amongst many videographers. Having said this, the ongoing critique of Panasonic's Contrast Detect AF makes no sense to most Lumix G9 photographers. In fact, the constant repetition of G9 auto-focus problems looks more like counter-marketing than information...
Technical conversations improve our knowledge and are critical in finding our way through the web of bogus information spread by fanboys, unworthy reviewers, and forum experts (promoters).
Pen F with 17mm f1.8 lens - ISO800, f5.6, 1/60 - Raw and Autumn Color Profile (V2) done in WS
Why don't we learn much from the ISO comparisons in camera reviews? Because technical equivalence is critical when comparing digital cameras and sensors. See this example. Andrew is one of my favorite M43 wildlife photographers. What do you learn from his ISO examples?
Also, see my article about the DxOMark sensor (image quality) database.
While newer sensors continue improving, the new G9 II high-resolution sensor and processor upped the G9 II's perceived IQ while maintaining the older G9's noise performance. Andrew mentions a 2-Stop ISO and 1-Stop base ISO improvement. The smaller and likely less efficient pixel area of the new 24MP sensor makes it hard to justify a +2-stop ISO efficiency. This means the G9 II's improvements could be like the previous G9's noise performance (Fig. 1), and the G9 II's lower base ISO might slightly up its Dynamic Range. Andrew also showed the importance of a steady platform by using a tripod.
Olympus EM1 MKI w 12mm f2.0 lens - ISO250, f8.0, 5 Sec (tripod) - Enhanced Raw File converted in WS and the 16-bit Tiff file edited in PS.
Why are small M43 lenses presented as having quality irregularities? Forum experts and reviewers often caution folks about M43 lenses because they are "known" for problems like soft corners, flaring, off-center focusing, and lens diffraction. See this discussion. These experts repeatedly recommend the Olympus 12 - 100mm F4.0 Pro lens. Does its "size/weight" support the transition to full-frame cameras? A quick search tells us Olympus and Panasonic factories are ISO9001 certified. ISO9001 is a manufacturing and quality standard used by quality-conscious manufacturers like Olympus.
Can we trust the advice from reviewers and forum experts? Watch this introduction to unethical marketing techniques like Astroturfing. I appreciate why full-frame marketers like to prevent M43 photographers from raving and enjoying positive feedback on M43 lenses like the Lumix 35 - 100mm f2.8, the Lumix 45 - 175mm, or the Lumix 7 - 14mm f4. The tiny Vario PZ 45 - 175mm f4 to f5.6 is one of the most criticized M43 lenses. I never experienced quality issues from multiple copies of this "fast" pocket-sized 350mm zoom lens. Another example of Astroturfing and questionable info about M43 lenses are the Olympus Premium Zuiko 12mm f2.0, 17mm, and 25mm f1.8 lenses...
Where does one find reliable info? Photo services like Flickr are helpful. Find the lens you like to buy and study the images taken with this lens. As an example, see the Olympus 25mm f1.8. This will help you to learn how any lens performs, plus photos are free from marketing noise...
Pen F with 17mm f1.8 lens - ISO320, f5.6, 1/60 - Raw conversion and the Autumn Color Profile with WS.
The M43 segment has many more examples of excellent compact lenses. The Leica 25mm f1.4, the Lumix 20mm f1.7, and the Zuiko 75mm f1.8 resemble only a few. For example, the Zuiko 9-18mm f4 is one of the finest ultra-wide lenses in its size and weight category. We should celebrate the high-quality M43 lenses by the various M43 lens manufacturers. I received my free 17mm Pro lens with my EM1 III and might sell it because I always reach for my trusty Zuiko 17mm f1.8.
Why don't I buy Pro M43 lenses? The short answer is size and price. For example, I had my 12-40mm F2.8 Pro lens for years. It's an excellent lens, but I hardly ever use it. The 12-45mm f4 Pro lens was an instant hit in my camera bag with its small size and excellent image quality. Olympus Pro Lenses are perfect for demanding wet and dusty applications, with their fast apertures and +/-2% better IQ. Standard and Premium Zuiko lenses are slower but deliver fantastic image quality.
I used new plus used Premium and Standard Zuiko lenses for years and NEVER had any major quality issues.
Why were the Pen F and the E-P7 cameras unique? These were the only Olympus cameras with advanced color and monochrome features. The Enhanced Raw Format and WS took these Color features to the next level with the new Luminance and Hue adjustments in Workspace. It also lets us share our Pen F and EP-7 Color and Monochrome adjustments (profiles) with M43 photographers.
Grassroots forum experts and reviewers highlighted the placement of the Creative Dial while ignoring the unique color and creativity functions of the Pen F and E-P7. Many M43 photographers thought the Pen F's creativity and color features were toys because forum experts repeatedly "promoted" them as gimmicks. The EVF and IBIS were also gimmicks in the DSLR days. The result is these color features were canceled. The E-P7 and the Pen-F are perfect for creative street and city projects...
The image was taken with the EM1 III, the 45mm f1.8 lens, a small product studio, and 2 Olympus FL600 flashlights in RC Mode.
Why should we own a flash and tripod? I understand why some would say they don't need a tripod or flash because IBIS and the camera's ISO performance are that good. What if a tripod or flashlight is the difference between excellent and average results? Why do we benefit from a sturdy platform, a flashlight, or the know-how to do flash photography? I saw this interesting video from Chris Baitson using his tripod and LED light while doing macro photography.
See this information from Olympus on flash photography - link.
See this video discussing macro photography and using a flash - link.
See this excellent video on using a flash for portrait photography - link.
Olympus E450 (10MP) with 50-200mm f2.8-f3.5 lens - ISO100, f8.0, 1/250 - Enhanced Raw converted in WS.
Why is it necessary to review the benefits of having a tripod, flashlight, or LED panel in 2023? Only a few apply the benefits of more light, flooding a sensor, or upping the sensor's saturation. Tripods and flashlights are perfect for poor lighting situations. For example, a tripod provides a stable platform for sharper landscapes, macro, product, and blue hour or nighttime scenes. Accept for heat, longer shutter speeds do not negatively impact the sensor's saturation process? It's better to use a tripod and shutter speeds of +10 seconds for nighttime city scenes than upping the ISO...
2. Let's review a few examples
Our aim with these examples is to demonstrate how one improves the sensor's Saturation and SNR. The challenge is the differences between highlights and shadows. The various surfaces and luminance levels (shadows) reflect different light intensities to the sensor. The goal is to reduce noise and increase tonal data by pushing the sensor's Saturation and SNR.
The above example shows two methods for upping the sensor's saturation and SNR in the shadows. Although ETTR worked well for the above image, I could not control the different parts of the scene. A flashlight allows us to illuminate (light source) the subject separately from the background. For example, a "fill-in" flash adds more control to the look and feel of our portrait images.
EM5 II with 12-45mm f4.0 Pro Lens - ISO200, f5.0, 1/1250
The above image is a typical landscape. The marked areas risk having more visible noise and less tonal data because the sensor receives less light from the shadow areas. My tripod provided a stable platform for my camera. Early morning scenes are more challenging with their deep shadows.
Always inform yourself about the different types of reflected light. For example, how do different colors or surfaces reflect the light? The mountain has less reflected light than the water or houses. Less reflected light means a lower SNR. Deep shadow areas reflect very little light onto the sensor.
E-P7 with 17mm f1.8 lens - ISO200, f4.0, 1/50 - Raw converted in WS
I used a fill-in flash to saturate the sensor for the person in the above scene. That means the person is noise-free because the flash improved the sensor's saturation in that area. The flash also balanced the inside and outside exposure levels. This is only possible with an artificial light source.
I typically set my flash output manually to prevent the flash from overpowering the scene. A smaller flash output does not disturb others and doesn't need diffusers or special techniques to keep the subject from glaring or overexposing. This technique takes practice to work well...
Olympus EP3 with 75mm f1.8 lens - ISO400, f1.8, 1/160 - Raw converted in WS.
The above image is unique because the older E-P3 had a new 12MP sensor and a TruePic VI Due Core Image Processor. It's a step above the previous models, but having an older sensor, we can expect more visible noise (noise floor) than more recent M43 cameras. I upped my shutter speed and used ISO400, an aperture of f1.8, and -0.7EV to improve my image sharpness. I lowered the SNR with a -0'.7EV exposure compensation and a 1-stop (ISO400) image signal amplification.
Being a handheld image, I knew the sensor was less saturated with likely more visible shadow noise. I know the noise filter in Workspace works well, and I only had to select the "Low" option for this example. My camera settings were not ideal, but I could up my shutter speed by keeping the ISO low with an exposure compensation of -0.7EV. The E-P3 is fully compatible with the Enhanced Raw Format and WS. I also relied on the EP3's improved IBIS and the excellent 75mm f1.8 lens...
EM1 III with 12-45mm f4 - ISO1000, f5.6, 1/1600 - Raw file converted in WS.
We are blessed with cold weather and lots of snow this year. I opted for my EM1 III as we walked the dog. I had the previous model for 6 years when OM-System did a special on the Olympus EM1 III with the 17mm f1.2 lens. I mistakenly assumed the MKII and MKIII were the same because they use the same sensor. What a surprise when the Olympus EM1 III became the finest M43 camera I ever owned. Its image quality is fantastic, and the TruePic IX Image Processor is brilliant. It feels like using a completely different camera. As you can see (above image), it was sunny with reflecting surfaces and high dynamic range areas. I used my Polarizing filter to tone down the highlights...
Olympus EM1 III with 25mm f1.8 Zuiko lens and the FL300 Flash.
As said, the EM1 MKII and III use the same sensor. This is important because the MKII was launched in 2016. Even though DxO rated this the best M43 sensor in 2016, the actual sensor is at least 10 years old. While the EM1 III's low-light capability is relatively good, it can't compete with newer sensor & processor combos. Knowing that, how does one improve its low-light performance? The answer is preparation, manual exposure, and focusing on saturating (optimizing) the sensor.
I used the following camera settings:-
- ISO1250 (I knew I could use AI noise reduction, and it's available from ISO800 in WS)
- 1/200 Shutter Speed (This is the lowest shutter speed to "freeze" movement)
- I controlled my flash by varying its output between -1/3 to -1EV
- I "sacrificed" DOF to control the light with my aperture
The flash enabled me to increase my shutter speed as it added a new variable to my exposure mix. The flash helped me to drastically improve my low-light image quality, even though I couldn't saturate the sensor. The reduced output of the FL300 gave me a "friendly" or less intrusive light source. I managed the intensity and reach of my flash with my ISO and aperture combinations...
Olympus EM1 III with 12-200mm, ISO200, f7.1, 1/640, -1.3EV - Raw converted in PL6
How would one plan the above photo? Consider your exposure strategy, unique camera settings, focusing plan, and the raw file conversion/editing when capturing the above scene. Consider the reflective properties of surfaces plus the reflected intensity (energy) of various colors. Use the sensor's saturation characteristics (SNR) and what you can do to improve the shadow information, knowing that all digital cameras (sensors) benefit from knowledge and planning...
Olympus E400 (10MP, CCD) with 25mm f2.8 lens - ISO100, f7.1, 1/100 - Jpeg with an analog feel prepped in WS. It's my favorite iMac wallpaper.
Conclusion
The first step in improving my IQ was to master my camera. The various computational features of my Olympus cameras meant nothing if I couldn't select and apply features like Live ND, Pro Capture, and Live Composite. The technical aspects reviewed in this article were the 2nd step in improving my image quality. The 3rd step was walking away from social media "experts" and undisclosed (paid) camera reviews. I learned to trust my camera and the brand I selected. For example, I always have my camera ready and use every opportunity to photograph.
It takes only a moment to learn how marketers say anything or contract services like Astroturfing to sell more products. It also takes only one incident or technical discussion to realize what we always expected is, in fact, happening. There is always a reason for social media or the news industry to hype about things. For example, why do we see so many OM-1 and XT-5 concerns and quality reports from presumably "grassroots owners?" Does this X-T5 report explain why..?
I continue to learn new things, like the Reflective Qualities of light, surfaces, and colors. You will find that the theoretical principles discussed in my articles are always the same. In other words, saturating the sensor or increasing the SNR is always applicable. I am currently studying 2 relevant books in German. Search for "Light and Exposure" by Michael Freeman or "Light and Exposure with 50 Questions" by Chris Weston. These books are great and will help any photographer...
Best and God's Bless.
Siegfried